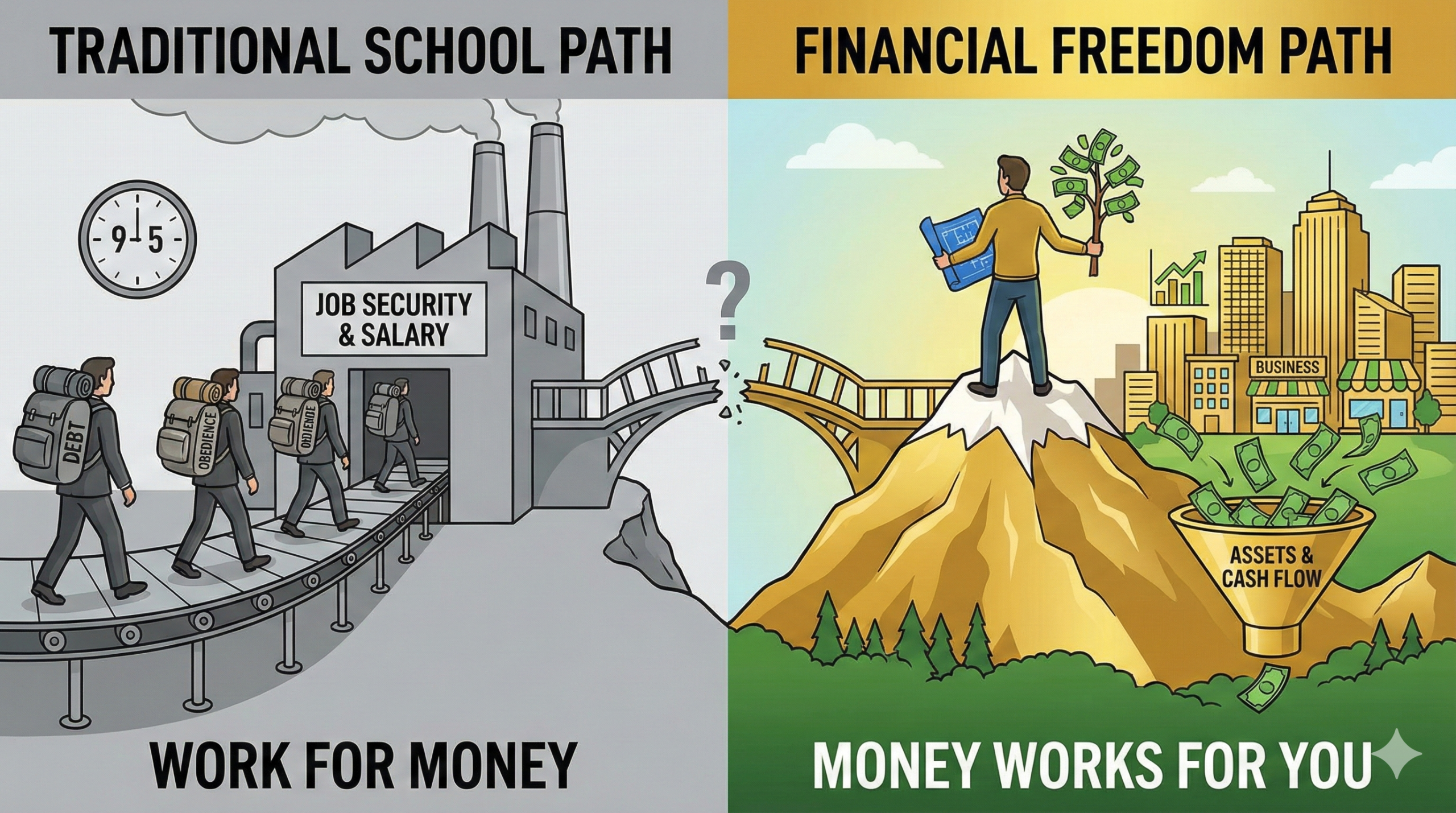
Why don’t schools teach us how to make money? You’ll be surprised when you find out the real reason behind it.
क्या आपने कभी सोचा है कि हम स्कूल में इतिहास, भूगोल और विज्ञान तो पढ़ते हैं, लेकिन “पैसा कैसे काम करता है” यह कभी नहीं पढ़ाया जाता?
यह कोई गलती नहीं है। इसके पीछे एक बहुत बड़ा और आसान सा कारण है: “अगर लोग सच में पैसे को समझ जाएँ, तो उन्हें इस सिस्टम की ज़रूरत ही न पड़े।”
यह बात सुनने में थोड़ी कड़वी लग सकती है, लेकिन यही सच्चाई है। आज हम उस सच से पर्दा उठाएंगे जो आपको आर्थिक रूप से आजाद (Financially Free) होने से रोक रहा है।
1. स्कूल का असली मकसद: कर्मचारी बनाना, मालिक नहीं
आधुनिक शिक्षा व्यवस्था का डिज़ाइन आपको अमीर बनाने के लिए नहीं किया गया था। कार्ल मार्क्स और पुरानी औद्योगिक सोच का प्रभाव आज भी हमारे स्कूलों पर दिखता है।
इस सिस्टम का मकसद सिर्फ ऐसे लोग तैयार करना है जो:
- समय पर ऑफिस आएँ।
- चुपचाप निर्देशों का पालन करें।
- प्रमोशन और सैलरी बढ़ने का इंतज़ार करें।
- और पूरी जिंदगी पेंशन या सरकार के भरोसे रहें।
स्कूल आपको “आज्ञाकारी” होने का इनाम देते हैं, न कि कुछ नया सोचने का। वे आपको “रटना” सिखाते हैं, “सोचना” नहीं। इसीलिए स्कूल से ‘कर्मचारी’ निकलते हैं, ‘उद्यमी’ (Entrepreneurs) नहीं।
2. मेरे दो पिता: एक ने दी सुरक्षा, दूसरे ने दी आज़ादी
मेरी ज़िंदगी में दो तरह की सोच का प्रभाव रहा।
- मेरे गरीब पिता: वे बहुत पढ़े-लिखे थे, पीएचडी होल्डर थे और सरकारी नौकरी करते थे। वे कहते थे— “कड़ी मेहनत करो, पैसे बचाओ और एक सुरक्षित नौकरी लो।” वे मानते थे कि सरकार उनका ख्याल रखेगी।
- मेरे अमीर पिता: वे कम पढ़े-लिखे हो सकते थे, लेकिन वे आर्थिक आज़ादी (Financial Freedom) में विश्वास रखते थे। उन्होंने मुझे सिखाया— “पैसे के लिए काम मत करो, बल्कि पैसे को अपने लिए काम पर लगाओ।”
यही एक लाइन सब कुछ बदल देती है। एक सोच आपको ज़िंदगी भर नौकरी में फंसाए रखती है, और दूसरी सोच आपको मालिक बनाती है।
3. अगर स्कूल ‘पैसे’ के बारे में सिखाते तो क्या होता?
ज़रा सोचिए, अगर हमारे सिलेबस में वित्तीय साक्षरता (Financial Literacy) होती, तो समाज कैसा होता?
- लोग रिटायरमेंट फंड या नौकरी को ही “सुरक्षा” नहीं मानते।
- लोग यह पूछते कि “मेरे पैसों को असल में कंट्रोल कौन कर रहा है?”
- कर्ज़ (Loan) डरावना नहीं लगता, क्योंकि लोग जानते कि “अच्छा कर्ज़” (Good Debt) और “बुरा कर्ज़” (Bad Debt) क्या होता है।
- लोग सिर्फ मार्केट बढ़ने की उम्मीद नहीं करते, बल्कि अपना खुद का कैश फ्लो (Cash Flow) बनाते।
4. सिस्टम आपको ‘आज़ाद’ क्यों नहीं होने देना चाहता?
सच यह है कि आज़ाद लोगों को कंट्रोल करना मुश्किल होता है।
जिस दिन आप पैसे की ताकत को समझ जाते हैं:
- आप बाज़ार गिरने पर घबराते नहीं हैं।
- आप सरकार से मदद की भीख नहीं मांगते।
- आप नौकरी जाने के डर से सहमे नहीं रहते।
सिस्टम को ऐसे लोग चाहिए जो डरे हुए हों और सैलरी पर निर्भर हों। इसीलिए वित्तीय शिक्षा को जानबूझकर ‘वैकल्पिक’ (Optional) रखा गया है। इसकी कोई परीक्षा नहीं होती।
5. अब आपको क्या करना चाहिए?
यह सब समझने के बाद आपके पास दो रास्ते हैं। या तो आप पुराने रास्ते पर चलें और सैलरी बढ़ने का इंतज़ार करें, या फिर अमीर लोगों वाले सवाल पूछना शुरू करें:
- “पैसा असल में काम कैसे करता है?”
- “मैं अपनी ज़िंदगी का मालिक कैसे बनूँ, किराएदार नहीं?”
- “मैं सैलरी के पीछे भागने की बजाय एसेट्स (Assets) कैसे बनाऊँ?”
याद रखें, स्कूल आपको नौकरी दे सकता है, लेकिन आर्थिक आज़ादी आपको खुद सीखनी होगी। आज ही से सीखना शुरू करें, क्योंकि यही वह शिक्षा है जो सच में मायने रखती है।
अगर यह पोस्ट आपकी सोच को बदलने में सफल रही, तो इसे अपने दोस्तों के साथ शेयर जरूर करें। उन्हें भी इस “सिस्टम” की सच्चाई जानने का हक़ है!