The Cell: The Basic Structural and Functional Unit of Life
Every living organism — from the tiniest bacterium to the largest whale — is built from one or more cells. Cells are often called the basic unit of life because they are the smallest structures capable of performing all the essential functions that define living things. But what exactly does that mean? Let’s explore why the cell holds this title, the differences between types of cells, and the key principles of the cell theory that form the foundation of modern biology.
🧫 What Is the Basic Unit of Life?
The cell is the basic unit of life. It is the smallest structure that can carry out all processes necessary for life — including metabolism, growth, response to stimuli, and reproduction.
Just as bricks form the foundation of a building, cells form the foundation of every living organism.
There are two main types of organisms:
- Unicellular organisms (like bacteria) consist of a single cell.
- Multicellular organisms (like humans, plants, and animals) are made up of many specialized cells that perform unique functions.
🔬 Why Is the Cell Called the Basic Unit of Life?
The cell is called the basic unit of life because:
- All living things are made of cells. Whether single-celled or multicellular, cells are the building blocks of all organisms.
- Cells perform vital life functions. Every process that keeps an organism alive — from energy production to waste removal — happens inside cells.
- New cells come from pre-existing cells. This means life continues through cellular reproduction.
In simple terms, without cells, life would not exist.
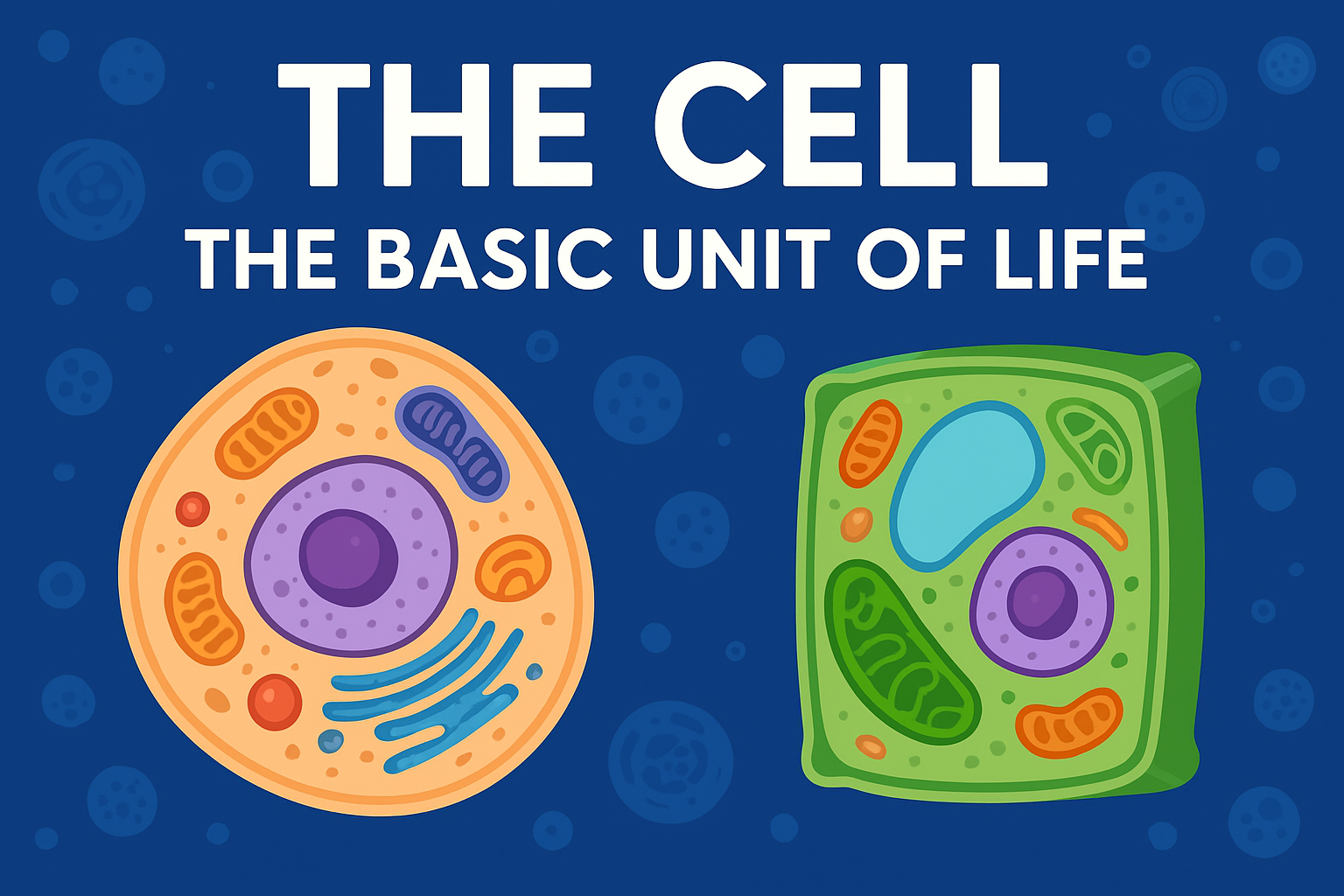
⚖️ What Is the Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells?
Cells can be classified into two major categories based on their structure:
| Feature | Prokaryotic Cells | Eukaryotic Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | No true nucleus (DNA floats freely in the cytoplasm) | Has a well-defined nucleus enclosed by a membrane |
| Organelles | Few or no membrane-bound organelles | Contains many organelles (like mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, etc.) |
| Examples | Bacteria and Archaea | Plants, Animals, Fungi, and Protists |
| Size | Smaller (1–10 µm) | Larger (10–100 µm) |
In summary:
Prokaryotic cells are simpler and evolved earlier, while eukaryotic cells are more complex and make up most of the organisms we see around us.
🧠 What Is the Basic Structural and Functional Unit of Life?
The cell serves both as the structural unit (it gives shape and form to living beings) and the functional unit (it carries out all life activities).
Just like organs in your body perform specific roles, different parts of a cell — such as the nucleus, cytoplasm, and cell membrane — work together to maintain life.
📜 What Are the Three Parts of the Cell Theory?
The cell theory is one of the most important principles in biology. It was developed in the 19th century by scientists Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolf Virchow.
The three parts of the cell theory are:
- All living organisms are made up of one or more cells.
- The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life.
- All cells arise from pre-existing cells.
This theory revolutionized biology by proving that all life shares a common building block — the cell.
🌱 Conclusion
The cell truly is the basic unit of life — the foundation upon which all living beings are built. Whether you’re studying single-celled organisms like bacteria or complex multicellular beings like humans, understanding how cells work helps us understand how life itself functions.
From the discovery of the first cell to the study of advanced cell biology today, this tiny unit continues to be at the heart of all biological science.